Fuel is one of the biggest expenses for many companies – it often makes it to the top of list of expenses that need tracking. Petrol or diesel is an integral part for fleet management, making up approximately 30% of the total fleet operating costs.
This article discusses the key strategies for increasing fuel efficiency while showcasing fuel tracking features offered through MyGeotab.
Being equipped with the right tools goes a long way in improving the overall performance. The following strategies can be considered for ensuring optimised fleet operations:
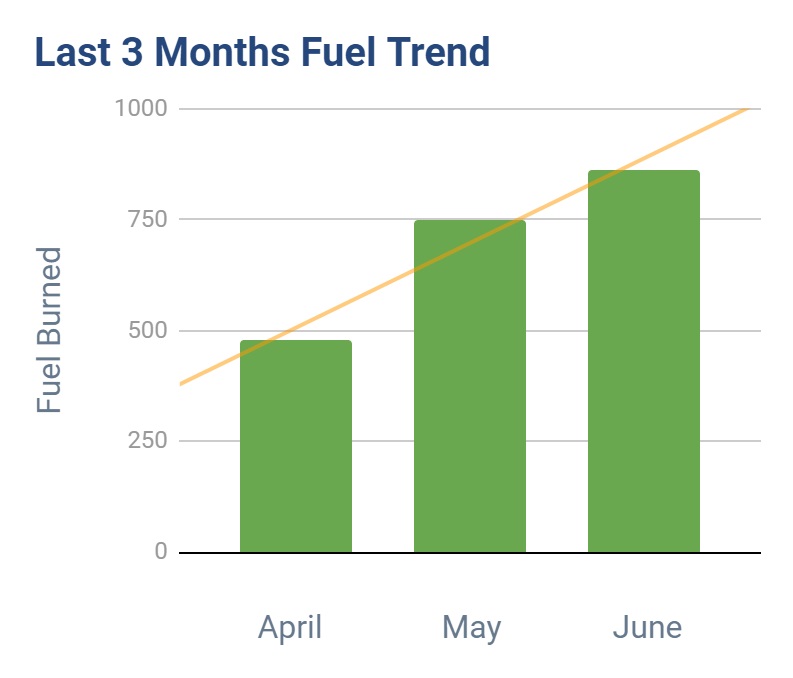
Bigger fuel wins? Compare trends
Look at the bigger picture. Ask the following:
- What has been our last three months fuel and idling trend?
- What’s our aggressive driving and kilometres driven trend?
Reducing idling, speeding and mileage will reduce fuel consumption. In this way, reviewing trend reports can help track progress. Cross-referencing different metrics provides useful insights and doesn’t separate your data into silos. Examining trendlines can be an indicator of whether programs are working, or not. Fuel usage that increases or remains flat indicates the ideal time to review and adjust the program.
Kilometres driven
Considering whether drivers are taking the most efficient routes or whether the fleet is dispatching the most efficient people for the call, is a contributor to fuel consumption. Geotab’s solution is ideal for managing km’s travelled, primarily because you will get full visibility into km’s and routes taken. Reducing km’s driven on a daily basis could potentially lead to more customer visits per day, helping you maximise your productivity. Geotab helps you make money while on the road, not spend money.
How Geotab calculates fuel usage
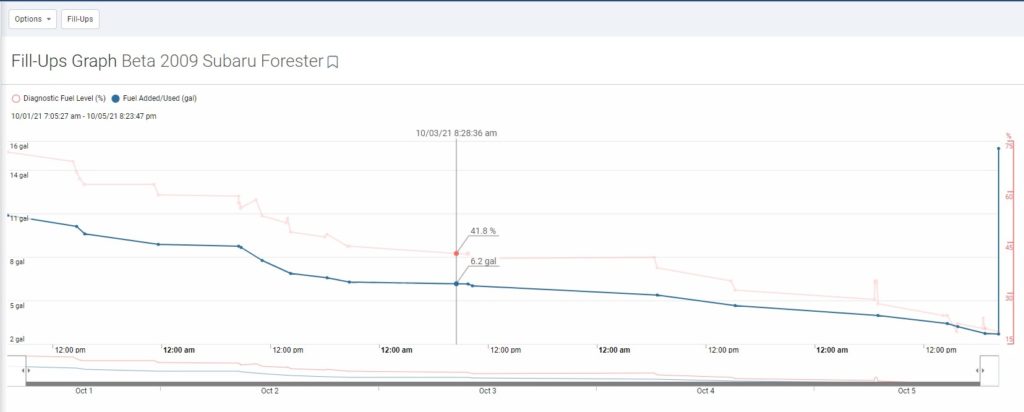
Our calculation: engine reported fuel data, imported fuel data and the GPS-calculated distance travelled. MyGeotab calculates for you the fuel used during a trip for a vehicle by querying the Device Total Fuel Used Metric from the engine. The fuel economy is then reported as the fuel amount used over the distance travelled with the given fuel (L/100 km).
How Geotab captures fuel data?
Depending on the protocol put in place, information is broadcast through the electronic control module (ECM) for some vehicles, while others require a request for data. In some cases, fuel must be calculated on our end, using other diagnostics like mass air flow.
Engine protocol refers to the language “spoken” by the vehicle’s engine computer module. Protocol is dependent on the vehicle’s make, model and/or year. Geotab supports the three main protocols used across industry (J1708, J1939, OBDII).
Where vehicles have difference protocols, we look at each on a case-by-case basis and use debug data to identify how to capture the fuel data and correctly report it. The accuracy in which we record fuel varies between 0.001L to 0.5L, depending on the protocol and how the engine broadcasts this information. For most vehicles, we can pull different types of diagnostics like trip, idle fuel used, fuel level, water in fuel and more.
Tracking fuel usage in MyGeotab
Fuel consumption is one of the top areas to target if a company is looking for ways to reduce costs. Money saved on fuel can be redirected to other business areas, such as human resources, operations, marketing, training or product development. The features available on MyGeotab fleet management software use processing power to create various dashboards, reporting on fuel usage and other areas of concern.
To learn more, take a look at these tools in MyGeotab. Helping fleets increase fuel efficiency and reduce overall fuel costs.
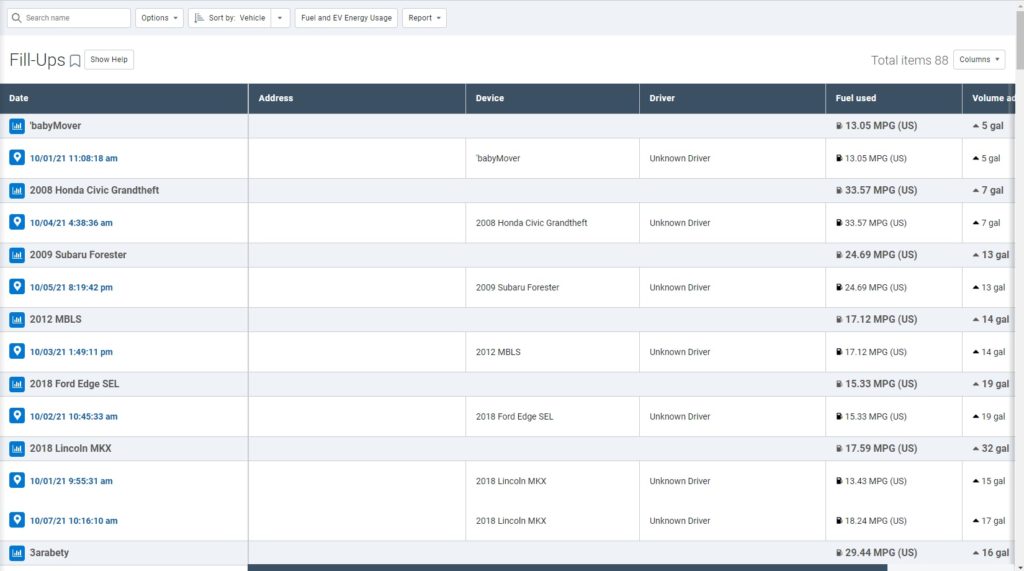
Fill-Ups report
The Fill-Ups report available can point you to unmatched fuel transactions that need further investigation. Telematics device fill-up data can report on imported fuel transactions.
Fleets can use their telematics data to validate fuel transactions. A fill-up event is defined as anytime fuel is added to the vehicle. The report will show you a brief summary, including total fuel added and total cost, for the time period you select.
How do we match fuel card data?
At least one of the below referencing fields can be used to match fuel transactions:
- VIN
- Device serial number
- License plate number
- Device description
- Device name
- Comments
MyGeotab accommodates any fuel transaction data, as long as it is in .csv or .xls file format. Fuel card importing is not tied to any specific manufacturer. Fuel transactions can be imported into your MyGeotab database via the Fuel Transaction Import Add-In or by using the API.
Geotab works continuously on fuel data output, to optimize accuracy and support for vehicles. Ongoing include support for European models, debug data to assist and develop calculations for non-petroleum vehicles and routine firmware updates containing fuel bug fixes and improved calculations.
Geotab Africa’s plug and play solution makes it easier for you to measure and manage your fuel usage. Identify any overconsumption and make an informed decision.









